Ontology¶
The Ontology Builder is a core TranzAI component that provides the capacity to reinforce model explainability, feature lineage, and develop graphs and causal inference.
TranzAI users have different options (not exclusive) to leverage the value of ontologies in data science:
- Capitalize on their domain knowledge to build their ontologies with the TranzAI ontology builder.
- Use a 3rd party ontology (particularly useful when data scientists have to consolidate data that already use a specific ontology and/or taxonomy).
- Use an ontology created by the TranzAI team.
The ontology builder is based on 3 core components:
- Entities
- Taxonomy
- Entity-relationships
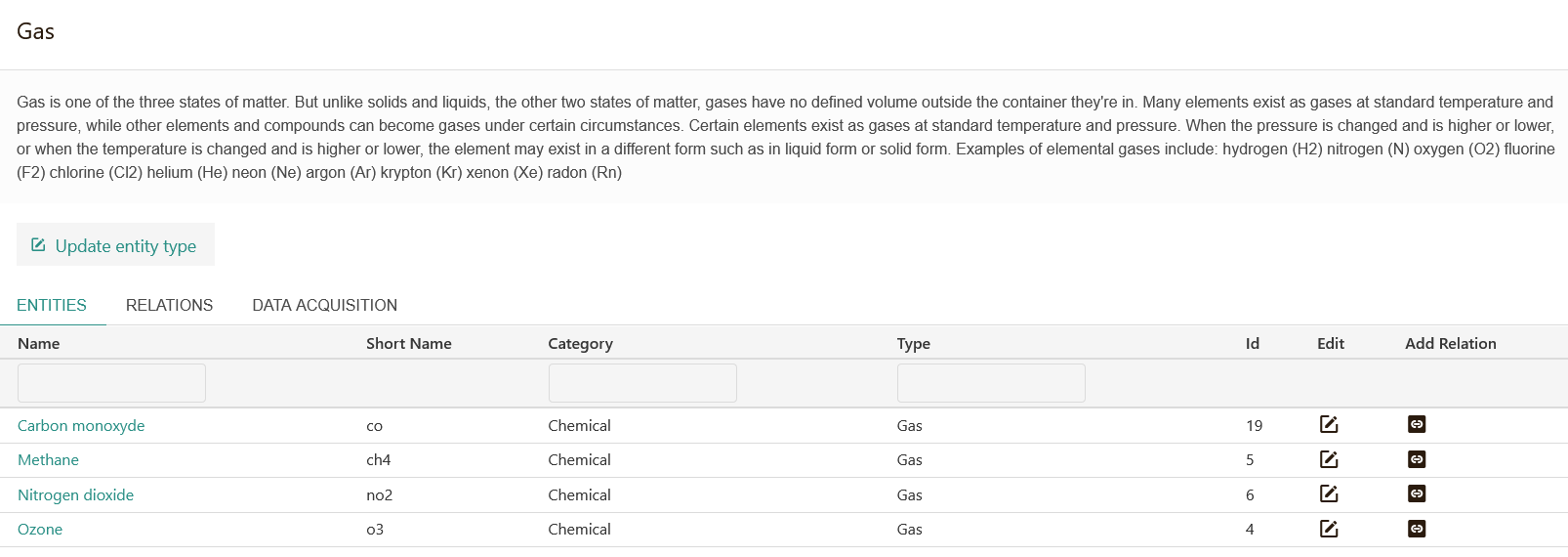
Entities¶
The following screenshot is an excerpt from the TranzAI Ontology for Climate Risk Analysis. Entities are created inside the core dimensions defined for this ontology (climate scenarios, climate models, temperature...).
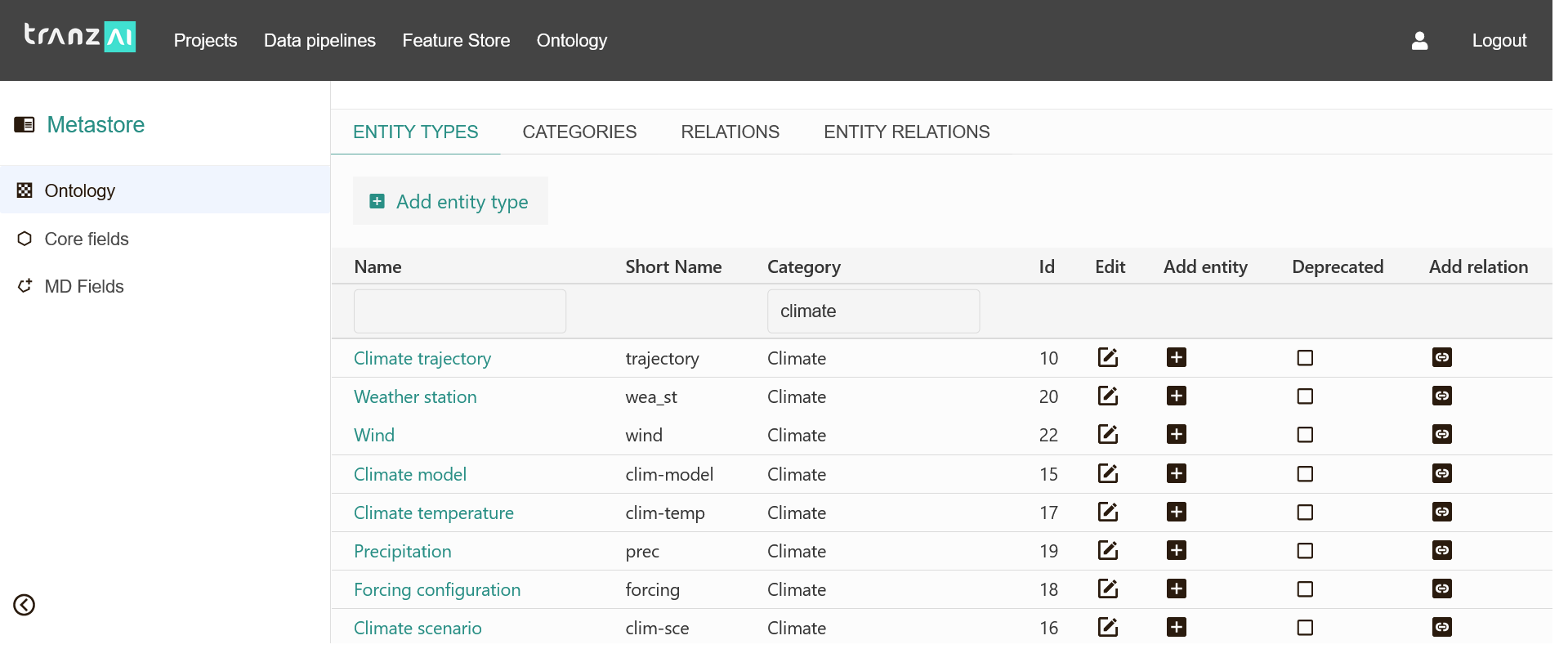
For each entity, you can provide a definition and its entity type. For each entity type, you can define a schema JSON that can be used to specify the information that should be stored for this type of entity.
Entity-relationship management¶
Relationships can be defined between your entities and your entity types to capture the way your system works and how entities are related to each other.
Integration of ontologies in the master data¶
At the master data level, you can build your features with the entities defined in your ontology. This is not an obligation but a good practice that will not only bring clarity to your master data from a semantic point of view but will also allow data scientists to deploy algorithms that can take advantage of the relationships that are part of the ontology.